V2 was recently engaged to build a foundational Agentic AI related governance security framework and controls set for a retail banking client.
The main outcomes were to proactively identify, assess and mitigate risks across the AI lifecycle, following related regulatory standards and compliance. This was to not only ensure a robust, secure and trustworthy system but to leverage Agentic capabilities of being more independent, accountable, intelligent, and potentially collaborative.
The engagement has created a baseline for banking vulnerabilities and threats within the evolving usage of Agentic AI. The client is aligned to architecture, privacy, authorisation and access (such as financial details, PII data, login credentials) privileges, and related controls that are scalable from a single agent to a more collaborative, multi-agent environment. The capabilities of Agentic AI to perceive, understand, decide and act are now better understood within the banking environment.
The project also covered the integration and tooling capabilities, using the banking institution’s internal systems and third-party products for continuous monitoring, discoverability, observability, operability and trust for authorised banking personnel.
Reasoning, Autonomy and Specialisation are Key
The core parameters in Agentic AI are reasoning, autonomy and specialisation as they drive efficient workflows and automation. In the retail banking industry, this will provide greater actions learned that meet key retail banking metrics with customers, staff, support and banking systems.
When organisations are building foundational core capabilities with governance, security and controls for Agentic AI, the organisation must understand critical touch points with Agent Archetypes and what will make them more enterprise-ready. For example:
The Agent Loop - A detailed understanding of knowledge, process and behaviours of specific agents including discoverability, access, knowledge and decisioning is required.
Agent Bootstrapping - The configuration and conditions need to be considered in which Agents follow a startup sequence to establish their identity, discover other agents, and prepare the tools and resources needed to fulfill tasks.
The Agent Types - Knowledge of agent capabilities including detailed sub types is required for meeting the intended agent architecture based on requirements.
The Agent Ecosystem - Understanding the specific environment in which an agent works, including the business and functional domains that it may reside in, operate to and transcend from.
Agent Assurance - Key areas of amplification and assurance understanding, which will include multiple agents and non-agents and processes. It must be visible to security control derivatives and the risk management framework.
Whilst this is not an exhaustive list, they are all key inputs when establishing an enterprise-grade capability that creates a robust, discoverable and trusted Agentic AI implementation.
The Agent Ecosystem
Agent archetypes within retail banking can connect to core workflows and processes across domains.
With Agents spanning transactions, cards, products, customers or payments, it can allow multiple ‘intra-domain’ or ‘inter-domain’ related agents known as ‘Agent Swarms’, acting autonomously but in coordination to complete Know Your Customer (KYC), fraud detection, customer service and many other related functions with high levels of automation.
Below is an example in Retail Banking where agents handle different parts of complex banking requests and tasks. These agents communicate with each other, share data and collaborate on processes in delivering a greater velocity and engagement through automation.
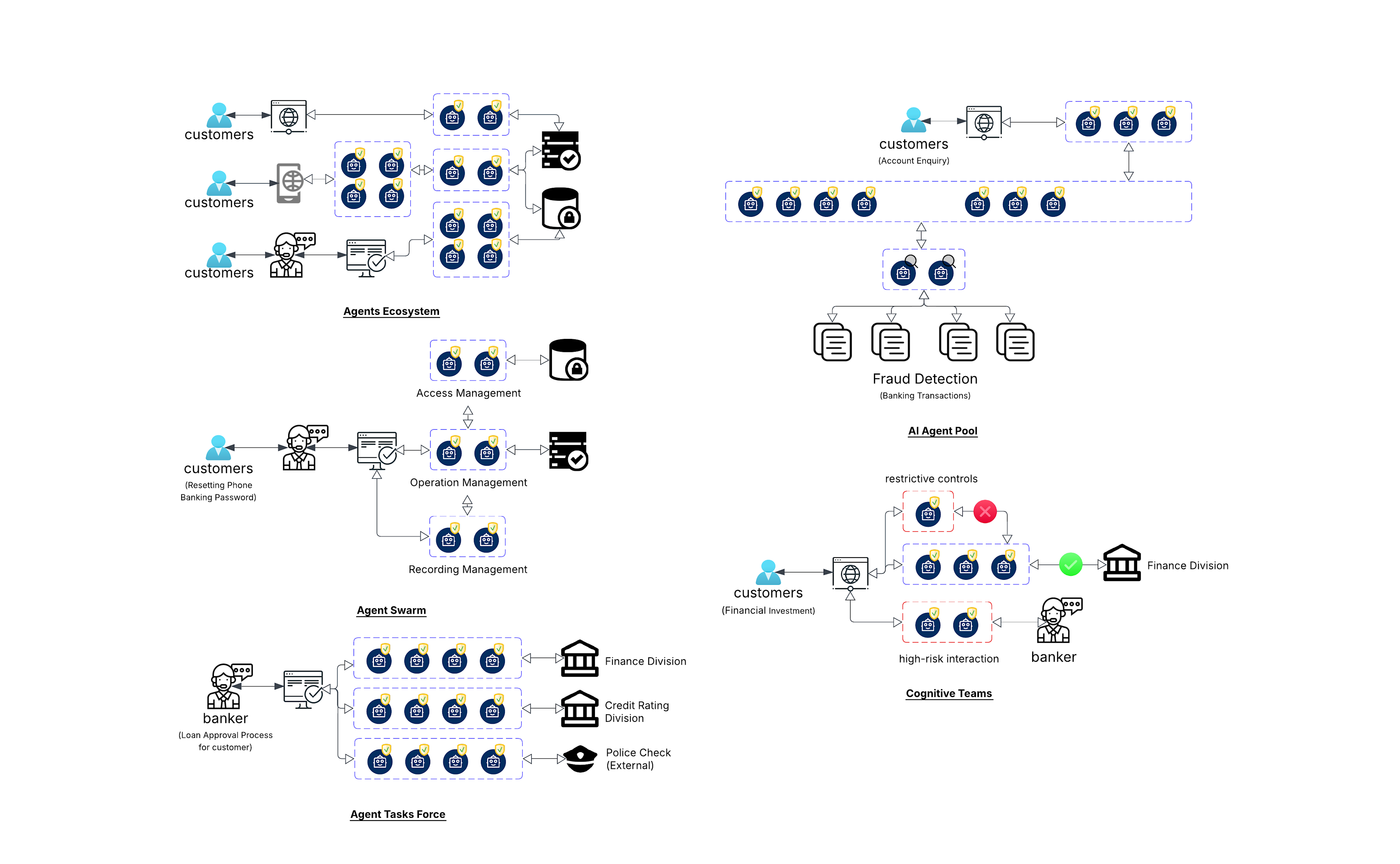
Further processes are being built, creating the start of deep customer experience - following up payments, providing pre-approved loans, processing queries and protection through fraud detection.
Agent Assurance
For these agents to work effectively, there needs to be resilience, consistency, visibility, and trust. AI threat modelling is a core requirement and MAESTRO (Multi-Agent Environment, Security, Threat, Risk, and Outcome) is a threat modeling framework uniquely designed for the challenges in AI. It can be used to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks throughout the entire AI lifecycle, connecting to initiatives and enabling the development of robust, secure, and trustworthy systems.
Other frameworks are focused on general security (STRIDE), risk-centric approaches (PASTA), privacy (LINDDUN) or organisational aspects (OCTAVE), so it’s important for organisations to align these correctly.
Amplifying Agentic AI in Retail Banking
Deep process capabilities in banking, systems thinking, coordinated business domain expertise and technical agent build and controls are vital aspects to helping amplify agentic AI in retail banking.
Enterprise-grade agents are essential to meet compliance, which take in all agent aspects with mapped controls, security and intelligence, including infra-as-code such as the Microservice or Container architectures in which they reside. They must comply with risk categorisation and management and be a retail business domain that is connected with an understanding of the key environments.
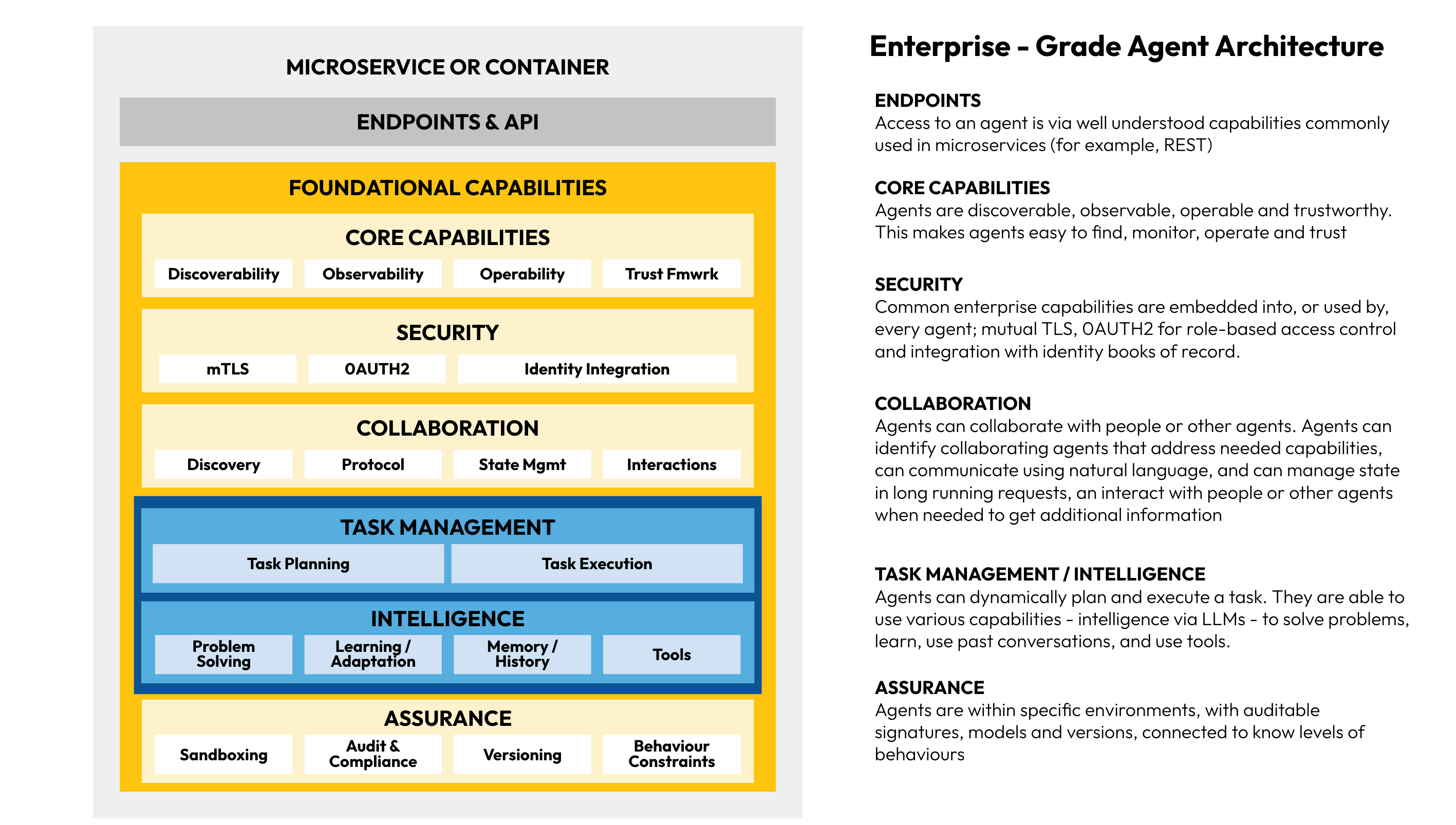
This is an example of the foundational technical capabilities within a Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) model.
Continuous monitoring, testing, notifications and automated controls are essential for maintaining compliance, security and quality outcomes when things don’t operate as expected.
Leveraging cognitive teams, where humans and AI work together as a blended, intelligent unit, enabling the creation of virtualised environments. These environments can produce digital twins that mimic production capabilities, allowing AI to perform at its best.
Creating Trusted Foundations with MAESTRO
As covered earlier in this article, Multi-Agent Environment, Security, Threat, Risk, and Outcome (MAESTRO) is a threat modeling framework uniquely designed for the challenges in AI.
A strong commitment is required to ensure AI systems maintain operational trust and consumer confidence for banking customers across MAESTRO dimensions:
Transparency and Explainability - All decisions made by AI systems have known decisioning, model lineage and signatures that banking professionals and regulators understand. They know the lineage in how and why decisions are made within agents, affecting workflows such as loan and credit approvals, escalations and anomalies. This allows all significant decisions impacting related banking assets and processes to be explainable as part of transparency to banking customers.
Clear Accountability and Governance - Oversight over AI actions requires removing errors, biases and misbehaviours as critical functions, especially in a regulated industry such as retail banking where AI decision-making can directly impact customer credit rating, customer scoring and customer profiling.
Discrimination Avoidance - Regardless of gender, race, age or any socioeconomics status, AI systems should operate independently and ethically to make decisions and judgements in maintaining system integrity and customer trust. Aligned ethical and responsibility judgements should occur for customers during functions and processes including loans, offering credit and recommending financial products.
Threats and Privacy - Sensitive customer data must be secured against threats and privacy risks. This would include multi-agent systems where no human interaction occurs for processing customer inquiries such as Account Balance, Resetting Passwords or Recent Transaction Inquiries to avoid breaches of data that would cause reputational damage and legal consequences for the organisation.
Operational Efficiency and Effectiveness - The implementation of AI systems must also improve efficiency within retail banking operations by streamlining processes, eliminating repetitive tasks, manual workloads and providing faster, more accurate responses and services back to retail banking customers.
Implementing with Confidence
There are various implementation examples for each of the principles of MAESTRO that are considered retail banking:
Clear Reasoning for Banking Customers, especially with regard to the rejection of customer loan applications. (e.g. Insufficient Income, Below Credit Scores) with a decision tree structure LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) or SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) towards meaningful user-friendly explanations.
Ethical Standards and no Deviations with AI agents, validating other AI agents through audits and logs aggregation on AI decisions to ensure it adheres with expected behaviours. This would also include validation and oversight from personnel within the retail bank to perform AI model audits to ensure AI performance and data are logged for review in case of disputes by customers.
All Sensitive Data Remains Secure and Protected through end-to-end encryption for all customer data. This is processed by compliance AI systems that ensure no unauthorised access (RBAC Implementation) and protect against cyber threats. All banking customer conversations must be encrypted with AI systems and only allow compliance AI systems access to perform their job functions.
Allow Customers to Effortlessly Self-Serve with the setup of dynamic hyperpersonalisation and insight capabilities. It uses AI agents to prioritise the right interface at the right time, with responses on real-time customer interactions data. Tailored solutions can be offered, such as adjusted payment plans or a financial advisor consultation if unforeseen circumstances change for existing loyal banking customers.
MAESTRO isn’t just a set of principles and frameworks but a way of ensuring that all AI systems remain a reliable tool in enhancing banking customer experience and services and decision-making within a retail banking environment.
Extending Trusted Controls to Trusted Autonomy and Workflows
Building trust within Agentic AI refers to the AI systems that are autonomous, responsible and capable of making decisions on behalf of the retail bank.
There are a number of Agentic AI use cases in the retail banking sector, where meeting high customer expectations and complying with complex regulatory standards are essential. These use cases highlight how Agentic AI can support retail banking operations while also emphasising the critical role of trust and governance in ensuring the integrity, compliance, and ethical functioning of AI systems.
Trust and governance considerations are fundamental across each use case, ensuring transparency, security, and accountability in the deployment and use of AI technology.
Increasing Customer Service and Support within Retail Banking (Chatbots & Virtual Assistants)
AI-powered virtual assistants handle banking customer queries. Helping banking customers to check account balances, inquire about recent transactions, reset passwords, or even assist with loan applications.
Trust & Governance: Communication and privilege rights between AI agents are encrypted and protected with sensitive data like personal financial details, account numbers, and login credentials from interception during transmission, with AI agents having the necessary privileges and rights to retrieve this information.
Improvement of Fraud Detection and Risk Management for Retail Banking
Agentic AI monitoring of customer banking transactions in real-time, identifying patterns and flagging suspicious activity with new fraud tactics and potential anti-money laundering activities.
Trust & Governance: Continuous Real-time monitoring and implementation of security controls following a set of governance frameworks towards anomaly detection and detection of malicious activity or fraud attempts. This could include tracking attempts to manipulate the AI into revealing confidential information or guiding users to external phishing sites.
Personalisation and Processing on Loan and Credit Decisioning for Retail Banking
Automation on faster loan approval by analysing banking customers’ credit history, financial data, and other relevant factors. It can also analyse banking customers’ needs and financial behavior to provide tailored loan products that are most relevant and affordable for each individual customer.
Trust & Governance: Ethical AI consideration within Agentic AI agents to ensure AI systems do not inadvertently introduce biases, which could result in discriminatory financial advice or unequal treatment of customers. Regularly test and adjust models to remove any form of bias. Furthermore, transparency of data usage allows banking customers to review and approve data usage policies governance by the retail banking.
Safe and Accurate Financial Management Advice for Retail Banking Customers
Usage of Agentic AI to provide banking customers with personalised financial advice based on their income, spending habits, and financial goals. It can also suggest budgeting strategies, investment opportunities, or ways to reduce debt.
Trust & Governance: Retail banking requires Credit Compliant AI agents in allowing financial recommendations to retail banking customers. Governance around controls and framework is required for humans and agents across all high-risks interactions and where AI systems cannot fully verify the identity of the customer or when sensitive tasks are involved.
Continuous Improvement / Uplifting of Retail Banking Regulatory Compliance in Retail Banking
Continuously monitor transactions and banking customer activities to ensure they are compliant with regulatory standards. It can help in real-time monitoring for violations of KYC (Know Your Customer), AML (Anti-Money Laundering), and other regulations through comprehensive audit trails and make it easier for retail banks to track transactions and meet regulatory requirements while also ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Trust & Governance: Agentic AI agents fronted by security products or services with the correct AI Operating Model to continuously monitor banking customers and retail banking operations activities with a Single Pane of Glass for transparency, traceability and accountability only to authorised security personnel.
Designing AI systems for retail banks that are explainable, fair, secure, and responsive will ensure that banking customers and users feel confident in the AI's capabilities, ultimately leading to a positive relationship with AI technology.
What’s Next for Agentic AI in Retail Banking
Agentic AI is a large focus for the team at V2, as we believe it is the next frontier in banking, innovation and governance for our customers. It is set to evolve in transformative ways in a very short period of time.
We believe that AI will feed a virtuous cycle. As the lines blur between traditional retail banking and FinTechs, AI will take on a larger role in the ecosystem. Traditional retail banking services will be embedded into non-financial platforms like retail sites, apps, and even social media platforms, offering financial services like loans, payments, and savings accounts. Agentic AI will further underpin and accelerate compliance, regulation, efficiency and customer experience.